 Go协程池深度解析:原理、实现与最佳实践
Go协程池深度解析:原理、实现与最佳实践
# 为什么需要协程池?
goroutine 虽然是轻量级的并发模型,但是协程也是有栈空间的,并且有上下文切换的开销,当协程数量增加时,性能可能会急剧的下降,甚至导致程序崩溃。
而协程池限制 gorotinue 的数量,并从共享的任务队列中提取任务执行,从而让 goroutine可控,不会超过其处理的能力,保证服务的稳定性。
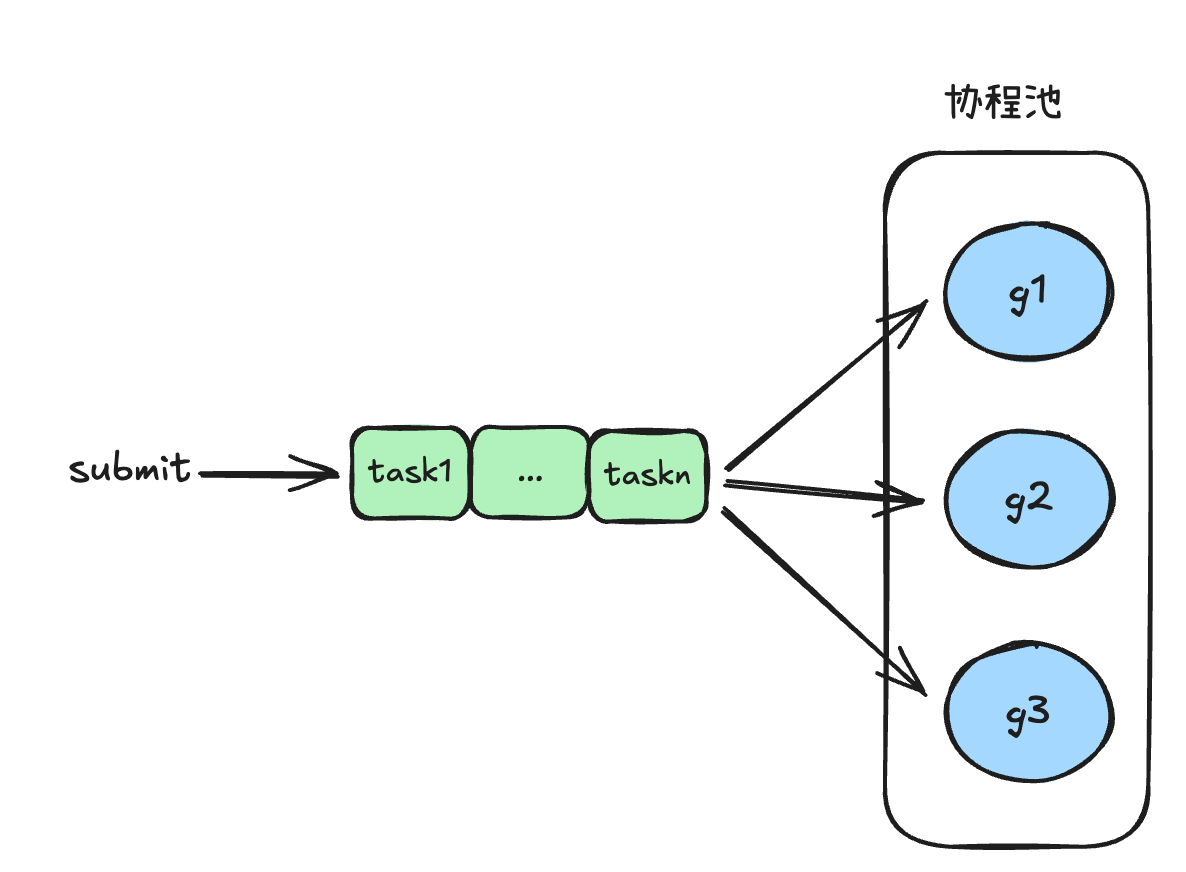
# 怎么使用协程池?
提前创建 5 个worker,再创建一个 jobs channel 用于传递任务,最后在不断地将任务生产到队列中,worker获取到任务后执行,最后将 jobs close掉,协程也就都退出了,最后程序退出。
func worker(id int, jobs <-chan int, results chan<- [32]byte) {
for j := range jobs {
results <- doWork(j)
}
}
func doWork(n int) [32]byte {
data := []byte(fmt.Sprintf("payload-%d", n))
return sha256.Sum256(data) //
}
func main() {
jobs := make(chan int, 100)
results := make(chan [32]byte, 100)
for w := 1; w <= 5; w++ {
go worker(w, jobs, results)
}
for j := 1; j <= 10; j++ {
jobs <- j
}
close(jobs)
for a := 1; a <= 10; a++ {
<-results
}
fmt.Println("ending")
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
可以自己实现,也可以直接利用已经实现好的开源协程池。
https://github.com/Jeffail/tunny
https://github.com/panjf2000/ants
https://github.com/bytedance/gopkg/tree/main/util/gopool
# Worker Pools 该设置成多大?
池中的协程最优的协程数量和 CPU 核数密切相关。可以使用 runtime.NumCPU() 或 runtime.GOMAXPROCS(0) 来获取 CPU 核数。
对于 CPU 密集型任务,通常工作协程数少于或等于逻辑 CPU 核数,可以让 CPU 利用率达到最大。而对于 IO 密集型任务,可以让工作协程数大于CPU核数,以为遇到 IO 会进行阻塞,也就是工作协程大部分时间处于阻塞状态。
# BenchMark
使用协程池和不使用协程池处理 10000 个任务的 BenchMark 比较
const (
numJobs = 10000
workerCount = 10
)
func doWork(n int) [32]byte {
data := []byte(fmt.Sprintf("payload-%d", n))
return sha256.Sum256(data)
}
func BenchmarkUnboundedGoroutines(b *testing.B) {
for range b.N {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(numJobs)
for j := 0; j < numJobs; j++ {
go func(job int) {
_ = doWork(job)
wg.Done()
}(j)
}
wg.Wait()
}
}
func worker(jobs <-chan int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
for job := range jobs {
_ = doWork(job)
wg.Done()
}
}
func BenchmarkWorkerPool(b *testing.B) {
for range b.N {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(numJobs)
jobs := make(chan int, numJobs)
for w := 0; w < workerCount; w++ {
go worker(jobs, &wg)
}
for j := 0; j < numJobs; j++ {
jobs <- j
}
close(jobs)
wg.Wait()
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
运行结果如下,使用协程池使用的资源更少,更快的完成工作。
$ go test -bench=. -benchmem .
goos: darwin
goarch: arm64
pkg: main/demo
cpu: Apple M4 Pro
BenchmarkUnboundedGoroutines-12 486 2501263 ns/op 639942 B/op 39754 allocs/op
BenchmarkWorkerPool-12 776 1540660 ns/op 320554 B/op 19758 allocs/op
PASS
ok main/demo 3.343s
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 什么时候使用 Worker Pools?
- 有大量或无限制的任务流处理。
- 为了程序的稳定性,限制并行操作的数量。
# 什么时候该避免使用 Worker pools?
- 对任务的延迟非常敏感,需要立即执行。
- 低负载的情况下,使用协程池反而增高了成本。
- 工作量较小并且是有限的。
上次更新: 2025/06/14, 16:16:07
